
You may notice the major drawback of acrylic when you see how easily it scratches or melts under heat. Acrylic surfaces often show marks from keys, tools, or cleaning pads. Heat can also damage this material. Standard acrylic starts to lose shape at temperatures as low as 75°C. For comparison, polyamide can handle up to 200°C. See the table below for details:
| Материал | Maximum Safe Operating Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|
| Acrylic Resin | 75-110 |
| Polyamide | 150-200 |
Other challenges include difficult repairs, low impact strength, and chemical sensitivity. Consider these factors before you choose acrylic for your project.
Major Drawback of Acrylic

Scratch Prone Surface
You will notice that the major drawback of acrylic is its surface. Acrylic looks clear and shiny when new, but it is more liable to scratching than many other materials. Even simple actions can leave marks. For example, wiping acrylic with a rough cloth or using the wrong cleaning method can create tiny scratches. Over time, these scratches build up and make the surface look dull.
Here is a table that shows the most common causes of surface scratches on acrylic:
| Cause | Описание |
|---|---|
| Daily Cleaning Practices | Improper techniques can create micro-scratches that accumulate over time. |
| Physical Contact | Interaction with hard objects can leave visible marks on the surface. |
| Environmental Factors | Dust and debris can act as abrasives when trapped between cleaning cloths. |
You may find that acrylic items in busy places, like schools or offices, lose their shine quickly. This happens because people touch or clean them often. If you compare acrylic to glass, you will see that acrylic is much more likely to show scratches. This major drawback makes it hard to keep acrylic looking new for a long time.
Tip: Use a soft, damp cloth and gentle soap to clean acrylic. Avoid using paper towels or rough sponges.
Limited Heat Resistance
Another major drawback of acrylic is its reaction to heat. Acrylic is not heat-resistant. If you place a hot object on an acrylic surface, you may see it bend or even melt. This can happen at temperatures that are not very high. For example, regular acrylic starts to soften at about 160°F (71°C) and may begin to deform at 320°F (160°C). Special heat-resistant acrylic can handle up to 90°C, but this is still lower than many other plastics.
| Temperature Range | Effect on Acrylic |
|---|---|
| 160°F to 210°F (71°C to 99°C) | Begins to soften |
| 320°F (160°C) | May start to deform |
| Up to 90°C | Heat-resistant acrylic maintains integrity |
You should remember this major drawback when you choose acrylic for kitchen items, lighting covers, or outdoor signs. If you use acrylic near heat sources, it may lose its shape or become unsafe. This is why many people pick other materials for places where heat is a concern.
When you look at the major drawback of acrylic, you see that it is both more liable to scratching and not heat-resistant. These two problems limit where you can use acrylic safely and keep it looking good. Other issues, like difficult repairs and chemical sensitivity, also matter, but scratching and heat resistance are the biggest reasons why people sometimes choose other materials.
Other Common Issues
Difficult Repairs
You may find that repairing acrylic is not easy. When this material gets scratched or damaged, you cannot simply buff it out like you might with glass. Deep scratches or chips often require special tools or even replacement. If you try to glue broken pieces, the seams may stay visible. This can make repairs look messy. Many people choose to replace damaged items instead of fixing them.
Low Impact Strength
Acrylic can break or crack when hit with force. You might see this happen if you drop an acrylic sheet or strike it with a hard object. The potential for cracking increases in cold weather or when the material is thin. This low impact strength is one of the main disadvantages compared to other plastics. You should avoid using acrylic in places where it might get hit or dropped often.
Environmental Degradation
Acrylic does not always hold up well outdoors. Over time, sunlight and pollution can change how it looks and feels. You may notice yellowing, brittleness, or loss of clarity. Several environmental factors can speed up this process:
- Ultraviolet (UV) light from the sun causes photodegradation and yellowing.
- High temperatures or direct heat sources can discolor and weaken the material.
- Pollutants, such as solvents and ammonia-based cleaners, can make acrylic degrade faster.
You can see the difference in outdoor lifespan between standard and UV-stabilized acrylic in this table:
| Type of Acrylic | Lifespan Outdoors | Optical Clarity After 10 Years |
|---|---|---|
| Standard Acrylic | 5–10 years | 88–90% transmission |
| UV-Stabilized Acrylic | 15–20 years | 88–90% transmission |
Chemical Sensitivity
You need to be careful with chemicals around acrylic. Some common cleaners and pool chemicals can cause damage or discoloration. For example, chlorine and bromine compounds, often used in spas, may bleach the surface. Tri-chlor tablets can lead to blistering and fading. Even household cleaners with ammonia can harm the finish. Always check labels before using any product on acrylic to avoid unwanted reactions.
Note: Using the wrong chemicals can shorten the life of your acrylic items and make them look old before their time.
Impact on Use
Everyday Applications
You see acrylic in many places every day. People use it for display cases, protective screens, and household items. Acrylic looks clear and bright when new, but it can show scratches quickly. If you use acrylic for a display case, you may notice marks from cleaning or touching. These scratches make the case look dull and less attractive. In kitchens, acrylic does not handle heat well. Hot pans or dishes can warp or melt the surface. This limits its use for kitchenware and lighting fixtures. You need to think about these disadvantages before choosing acrylic for areas where appearance and durability matter.
Here is a table showing common complaints from people who use acrylic in their homes:
| Complaint Type | Описание |
|---|---|
| Skin Irritation | All three chemicals are irritants to skin, eyes, and respiratory tract. |
| Allergic Reactions | Exposure can lead to allergic contact dermatitis, damaging nails and inflaming skin. |
| Long-term Health Effects | Potential risks include cancer and organ-system toxicity due to repeated exposure. |
Tip: If you want to keep acrylic looking good, use gentle cleaning methods and avoid placing it near heat sources.
Safety and Longevity
You should consider safety and how long acrylic will last before you use it. Scratches may only affect how the material looks, but they can make windows or screens less clear. Over time, these marks build up and reduce the beauty of acrylic installations. If acrylic gets too hot, it can become brittle and crack. This can lead to broken pieces and possible injury. You need to check the environment before installing acrylic to make sure it will stay safe and strong.
- Acrylic sheets are prone to scratching, which can affect their aesthetic appeal and clarity over time.
- Scratches may only cause cosmetic damage, but they can compromise the beauty of installations, such as acrylic windows.
- Acrylic is not heat-resistant; exposure to temperatures above 150°F can make it brittle and lead to cracking or breaking.
You should weigh these disadvantages against the benefits before you choose acrylic for your project. If you want a material that stays clear and strong for many years, you may need to look at other options.
Acrylic vs. Other Materials

Glass Comparison
You often see acrylic resin and glass used for windows, screens, and displays. Both materials look clear and shiny, but they behave differently when you use them every day. Acrylic resin scratches much more easily than glass. In laboratory tests, you can see the difference in haze after repeated abrasion:
| Материал | % Haze after 100 cycles |
|---|---|
| Plate Glass | 0.23% |
| ACRYLITE® Optical abrasion resistant (MR) acrylic sheet | 1.34% |
| Uncoated Acrylic Sheet | 26.88% |
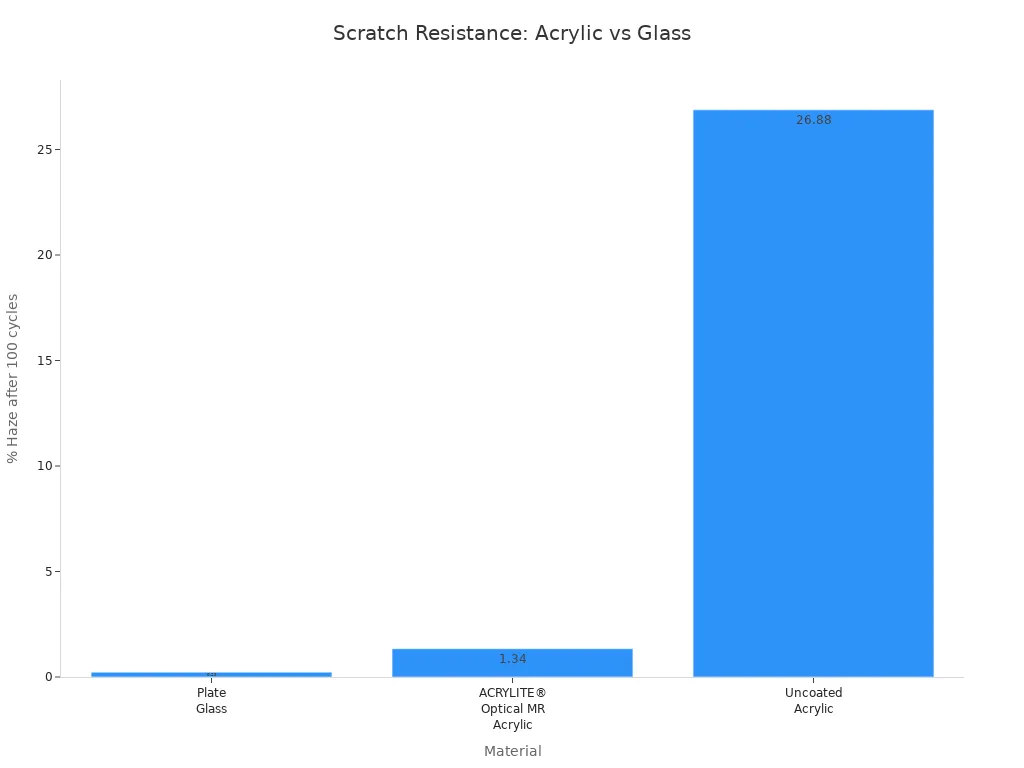
Glass resists scratches better, so it stays clear longer. Acrylic resin, especially uncoated types, can become cloudy and dull after cleaning or touching. When you think about heat, acrylic resin starts to soften at lower temperatures. Glass handles heat better, but it also transfers heat faster. Acrylic resin helps keep spaces cooler because it reduces temperature transfer by about 20% compared to glass. You may choose acrylic resin for areas where you want better temperature control.
Polycarbonate Comparison
You might wonder how acrylic resin compares to polycarbonate. Both materials are types of plastic, but polycarbonate is much tougher. In drop tests, polycarbonate can handle over 100 times more impact force than acrylic resin before breaking. This makes polycarbonate the best choice for safety gear, shields, and places where you need extra strength. Acrylic resin costs less, usually about half the price of polycarbonate sheets. If you need a budget-friendly option for displays or signs, acrylic resin works well. Polycarbonate costs more because it uses expensive raw materials and needs extra processing. You pay more for polycarbonate, but you get better durability and impact resistance.
Material Selection Considerations
When you pick a material, you need to think about your project’s needs. Acrylic resin is lightweight, so you can install it easily and save on transport costs. It is recyclable, which helps you manage waste responsibly. You can clean acrylic resin with mild soap and water, making maintenance simple. Acrylic resin lasts a long time, so you do not need to replace it often. If you need a material that resists scratches, handles heat, or survives strong impacts, you may want to look at glass or polycarbonate. Polymethyl methacrylate, also called pmma, is the chemical name for acrylic resin. You see pmma used in many products because it balances cost, clarity, and ease of use.
Tip: Always match the material to your needs. Consider clarity, strength, cost, and how easy it is to maintain.
Reducing Acrylic’s Drawbacks
Protective Measures
You can protect surfaces by using special coatings and treatments. These coatings help reduce scratching and chemical sensitivity. The table below shows some common options:
| Coating Type | Описание |
|---|---|
| UV-curable coatings | Create a hard, durable surface that resists scratches. |
| Polyurethane-based coatings | Offer flexibility and hardness for better abrasion resistance. |
| Silicone-based coatings | Add a tough layer while keeping surfaces clear. |
| Nanoparticle-reinforced coatings | Improve hardness and abrasion resistance without losing transparency. |
Acrylic latex paint works well in high-traffic areas. It resists cracking and peeling, so you see fewer signs of wear. You can use acrylic paints both inside and outside. These paints keep their color and stay clean over time. Pure acrylic resin in acrylic paints adds flexibility and durability. The breathable nature of acrylic paints prevents moisture problems, which helps on porous surfaces.
Tip: Choose coatings and acrylic paints that match your needs for durability and appearance.
Maintenance Tips
You can extend the life of your items with simple care. Use mild soap and water or cleaners made for acrylic paints. Avoid high-pressure washers, steam cleaners, and metal tools. These can scratch or damage the surface. Apply an acrylic protective film during installation to shield against scratches. Store sheets vertically in a cool, dry place. Use interleaving paper to prevent abrasion. Always lift sheets instead of dragging them.
Improper cleaning can cause micro-scratches and clouding. Acidic or ammonia-based cleaners may discolor or dull the surface. Paper towels and rough fabrics also create marks. Even some products labeled as safe for plastics can harm acrylic paints over time.
Note: Gentle cleaning and careful handling keep acrylic paints looking new.
Choosing Alternatives
You may want to look at other materials for better scratch resistance or heat tolerance. Polycarbonate offers higher heat resistance, with continuous use up to 239°F. Acrylic has higher surface hardness, so it is more scratch-resistant. Polycarbonate works well in places where you need impact resistance and durability under heat. Acrylic paints give you bright colors and a smooth finish, but they are softer and can collect dirt more easily.
When you think about the environment, acrylic paints have a smaller carbon footprint than many alternatives. However, their production still uses non-renewable resources and can cause water pollution. You should weigh the benefits and drawbacks before making your choice.
Callout: Polycarbonate is best for strength and heat, while acrylic paints are ideal for color and finish.
You now know that acrylic scratches easily and does not resist heat well. These drawbacks can limit where you use it. You should also think about other issues, like support needs, price, and aging. See the table below for a quick review:
| Drawback | Описание |
|---|---|
| High Support Needs | Needs strong support to prevent cracks |
| High Price | Can cost as much as premium materials |
| Aging | May fade or lose gloss over time |
Choose acrylic only if it fits your needs and you can manage these limits.
ЧАСТО ЗАДАВАЕМЫЕ ВОПРОСЫ
What makes acrylic scratch so easily?
Acrylic has a softer surface than glass or polycarbonate. Everyday items like keys or rough cloths can leave marks. You need to handle acrylic with care to keep it looking clear.
Can you repair scratches on acrylic at home?
You can fix light scratches with a special acrylic polish and a soft cloth. Deep scratches often need professional help or replacement. Always test products on a small spot first.
Is acrylic safe to use near heat sources?
No, acrylic does not resist heat well. Hot pans or lamps can warp or melt it. You should keep acrylic away from stoves, ovens, or direct sunlight.
How do you clean acrylic without causing damage?
Use a soft, damp cloth and mild soap. Avoid paper towels, rough sponges, or cleaners with ammonia. These can scratch or cloud the surface.
When should you choose polycarbonate instead of acrylic?
Choose polycarbonate if you need high impact strength or better heat resistance. Polycarbonate works well for safety shields, machine guards, and outdoor uses.
See Also
Understanding Impact-Modified Acrylic: Key Features and Uses
Exploring Acrylic Blocks: Definitions, Characteristics, and Applications
Acrylic Aquariums Explained: Definitions, Features, and Benefits
Acrylic (PMMA) Overview: Definitions, Properties, and Uses
Anti-Static Acrylic Explained: Principles, Definitions, and Uses


